How to resize partition in Windows Server 2012 R2
Updated on: October 29, 2024
To many people, it is not an easy task to change partition size for a server. The native Disk Management tool has “Shrink Volume” and “Extend Volume” functions to help resize partition in Server 2012 R2. But because of many shortages, you’ll encounter problem in many cases. When resizing Server 2012 partition with third party software, some people are worry about data safety. In this article, I’ll introduce how to resize partition in Windows Server 2012 R2 with Disk Management and the safest partition software.
Resize partition in Server 2012 r2 via Disk Management
The same with other versions, Windows Server 2012 has “Shrink Volume” and “Extend Volume” functions in Disk Management tool. Some people think that Windows native tool has best compatibility and safety. It is not true at least when resizing partitions. Disk Management is not 100% safe, it destroyed my partitions several times. If there are both primary and logical partitions on a disk, pay more attention. Comparing with server partition software, Disk Management has some shortages.
Shortages to resize Server 2012 partition with Disk Management:
- It can only resize NTFS partition, FAT32 and any other types of partitions are not supported.
- It cannot change the start position of a volume, therefore, it can only shrink a partition towards left and make Unallocated space on the right.
- If there are unmovable files in a partition, it can only shrink partition with little available space.
- When extending a partition, there must be adjacent Unallocated space on the right. Otherwise, Extend Volume option is grayed out.
If you don’t like to use third party software and you just want to shrink a NTFS partition, you may give Disk Management a try. To shrink partition in Server 2012 without software:
- Press Windows + X keys together and then click Disk Management.
- Right click a NTFS partition and select Shrink Volume.
- Click Shrink button to shrink this partition with maximum available space, or enter a specified amount by yourself.
Using Disk Management, you cannot extend a partition by shrinking another one. For example, after shrinking D drive, unallocated space is on the left of E drive and is nonadjacent to C drive, therefore, Extend Volume is disabled for both partition.
If you want to shrink FAT32 partition or extend a volume by shrinking another one, disk partition software is required.
Important note before resizing Server 2012 partition
1. Find out your disk partition structure
If you want to extend a partition by shrinking another one, these 2 partitions must be on the same disk, no matter to physical or virtual disk. If you open Files Explorer, you can see all partitions but you don’t know which partitions are on the same disk. Instead, you need to check in Disk Management.
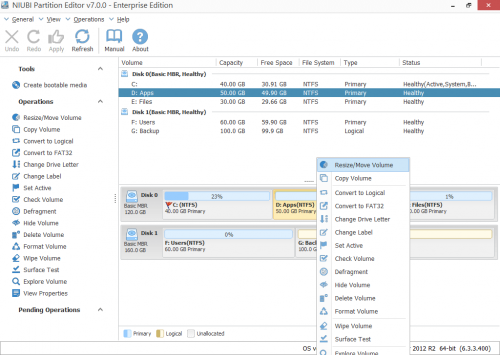
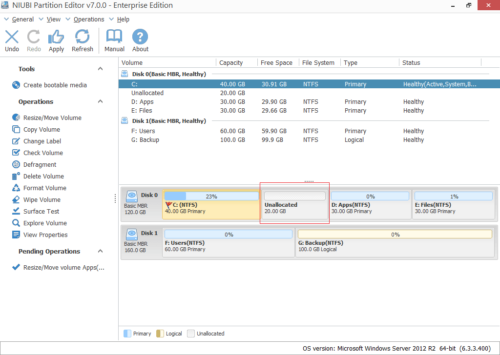
In Windows Server 2012 Disk Management console, you’ll see all disks with partition layout and detailed information of each partition, such as type, capacity and free space.
2. Take care of your system and data
It is good habit to make backup before any operation to a server. There’s potential system damage and data loss risk when resizing partition in Windows 2012 server. If you have no backup, you’ll lose data. If damage happens, it costs such a long time to restore. Therefore, it is very important to run safe software to resize Server 2012 partition.
Better than other tools, NIUBI Partition Editor 1-Second Rollback technology. If it detects error while resizing partition, it is able to revert server to original status automatically. Another major benefit is that it is much faster to shrink, move and copy partition. This is very useful if there are large amount of files in your server. With the help of Hot Clone technology, this software can clone disk partition without server interruption. You may clone system disk before any operation or regularly, when it is failed to boot, you can change to boot from the clone disk immediately.
How to resize partition in Windows Server 2012 R2
Step 1: Download NIUBI Partition Editor, right click a NTFS or FAT32 partition (here is D: drive) and select “Resize/Move Volume“.
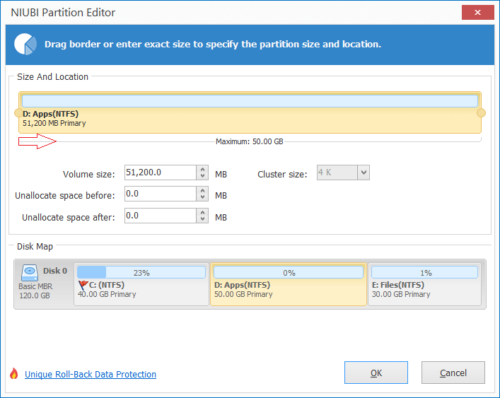
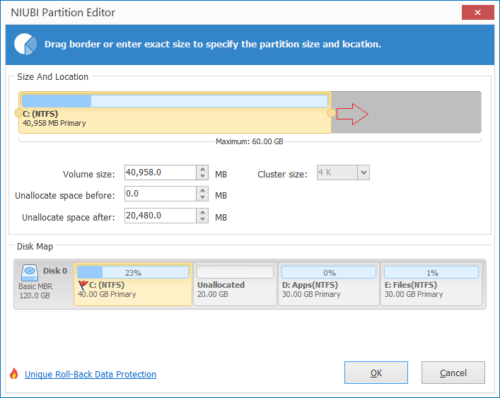
Step 2: In the pop-up window, drag the left border rightwards, or enter an amount in the box of “Unallocated space before”, Unallocated space will be made on the left of D drive. If you drag right border towards left, Unallocated space will be made on the right.
Click OK and back to the main window, there’s a pending operation listed on bottom left, click Apply to take effect.
You may also continue other operations and click Apply at last to execute all pending operations at one time. If you want to create more partitions, right click the Unallocated space and select “Create Volume”. If you want to extend partition, continue next step.
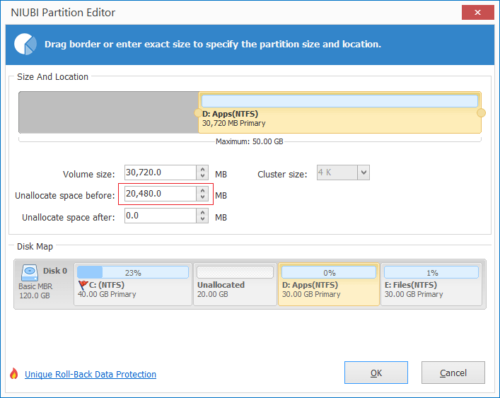
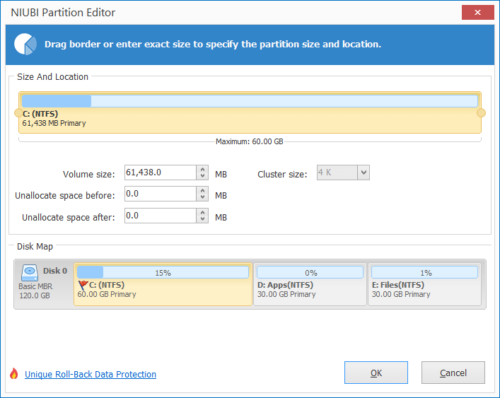
Step 3: Right click C drive and select “Resize/Move Volume” again. In the pop-up window, drag the right border rightwards to combine this Unallocated space.
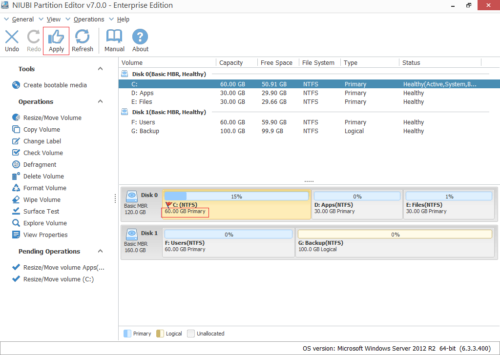
Step 4: Click OK and back to the main window, click Apply to take effect.
Tips when resizing partition in Windows Server 2012 R2:
- If you want to shrink D to expand E drive, you’d better make Unallocated space on the right when shrinking D. To do this, right click D and run the same “Resize/Move Volume”, in the pop-up window, you need to drag right border towards left.
- If you want to extend C drive by shrinking E, make Unallocated space on the left when shrinking E. Before merging Unallocated space to C drive, there’s an additional step to move partition D to the right.
- If you use any types of hardware RAID array or run Server 2012 as guest virtual machine in VMware/Hyper-V, there’s no difference, simply follow the same steps.
- If you want to extend a partition but there’s no available free space on the same disk, you can copy disk to a larger one and extend partition with extra disk space.
Video guide to resize partition in Windows 2012 server
Besides help resize partition in Windows Server 2012/2016/2019/2022 and previous Server 2008/2003, NIUBI Partition Editor helps you do many other disk partition management operations such as merge, copy, convert, defrag, wipe, hide partition, scan bad sectors, etc.